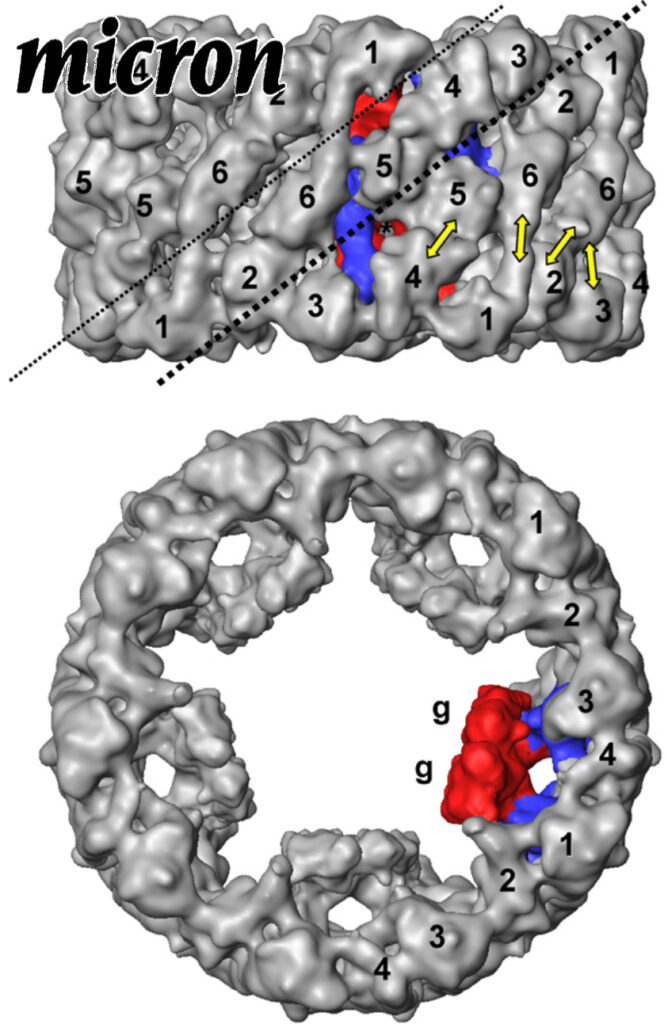
Comparative 11A structure of two molluscan hemocyanins from 3D cryo-electron microscopy.
Hemocyanins are giant extracellular proteins that transport oxygen in the hemolymph of many molluscs. Molluscan hemocyanins are cylindrical decamers or didecamers of a 350–400 kDa subunit that contains seven or eight different covalently linked globular functional units (FUs), arranged in a linear manner. Each FU carries a single copper active site and reversibly binds one dioxygen molecule. As a consequence, the decamer can carry up to 70 or 80 O2 molecules.
Comparative 11A structure of two molluscan hemocyanins from 3D cryo-electron microscopy. Read More »