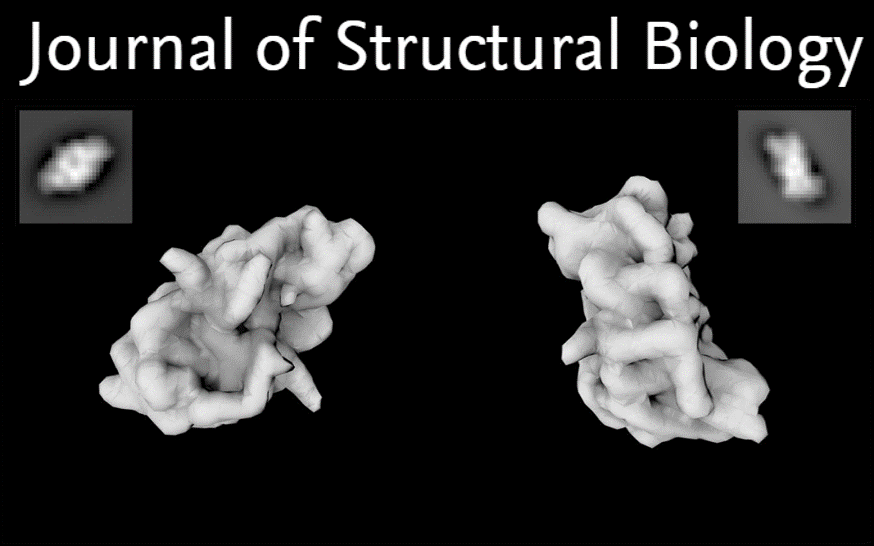
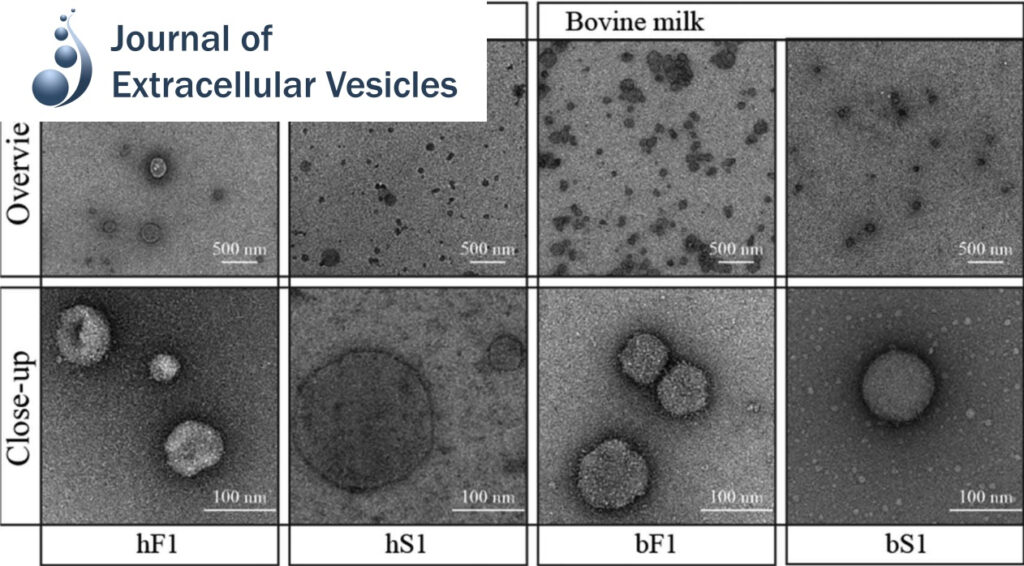
Conformation space of a heterodimeric ABC exporter under turnover conditions.
Our findings reveal that phosphate release, not ATP hydrolysis, triggers the return of the exporter to the IF conformation. By mapping the conformational landscape during active turnover, aided by mutational and chemical modulation of kinetic rates to trap the key intermediates, we resolved fundamental steps of the substrate translocation cycle of asymmetric ABC transporters.
Conformation space of a heterodimeric ABC exporter under turnover conditions. Read More »